The world of miniature vehicles is a fascinating realm, populated by two primary contenders diecast and plastic cars. These scaled-down models, loved by collectors and children alike, offer unique characteristics that cater to different preferences and needs. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of diecast vs plastic cars, exploring their history, manufacturing processes, advantages, and disadvantages. By the end, you’ll be well-equipped to determine which type of miniature car aligns best with your interests and requirements. Whether you’re a seasoned collector or a parent looking for a durable toy, understanding the differences between these two types is essential for making an informed decision.
What are Diecast Cars?
Diecast cars, as the name suggests, are primarily made using a die-casting process. This involves injecting molten metal, usually zinc alloy, into a mold to create the car’s body. This method allows for intricate detailing and robust construction. Diecast cars are renowned for their weight, durability, and realistic appearance, often mirroring actual vehicles with impressive accuracy. Collectors value diecast cars for their quality, detailed features, and investment potential. These miniature marvels represent a significant segment of the model car market, appealing to enthusiasts of all ages.
The History of Diecast Cars
The history of diecast cars dates back to the early 20th century, with the first models emerging in the pre-World War II era. Initially, these miniature cars were simple toys. As manufacturing techniques improved, so did the quality and detail. Companies like Dinky Toys and Corgi Toys became pioneers in the industry, producing a wide array of models that captured the imagination of children and adults alike. Over the decades, diecast cars evolved from simple playthings to highly detailed replicas, often becoming valuable collectibles. Today, the legacy of these early manufacturers lives on, and the market continues to thrive, with new models and brands appearing regularly.
Materials Used in Diecast Cars
The core material used in diecast cars is typically a zinc alloy, which is often combined with small amounts of other metals like aluminum and copper. This alloy offers excellent strength and allows for intricate detail. The wheels, windows, and interior components are often made from plastic. Paint and decals contribute to the final aesthetic. Some high-end models also feature rubber tires and metallic accents, adding to their realism. The combination of these materials results in a durable and visually appealing product.
Manufacturing Process
The die-casting process starts with the creation of a mold, which is a negative impression of the car’s design. Molten metal is injected into this mold under high pressure. Once the metal solidifies, the car body is ejected. The body is then cleaned and prepared for painting. Details such as headlights, taillights, and interior components are added. Finally, the model receives paint, decals, and other finishing touches to replicate the appearance of a real vehicle. This intricate process involves precision and attention to detail to achieve the high quality that diecast cars are known for.
Advantages of Diecast Cars
Diecast cars offer several compelling advantages, primarily centered around their durability and realism. Their weight and solid construction make them feel premium and contribute to their longevity. The detailed features, often including accurate interiors, engine components, and realistic paint finishes, make them highly sought after by collectors. Moreover, the investment potential of certain models adds to their appeal. These factors make diecast cars a popular choice for enthusiasts who value quality, detail, and the potential for long-term value.
Durability and Longevity
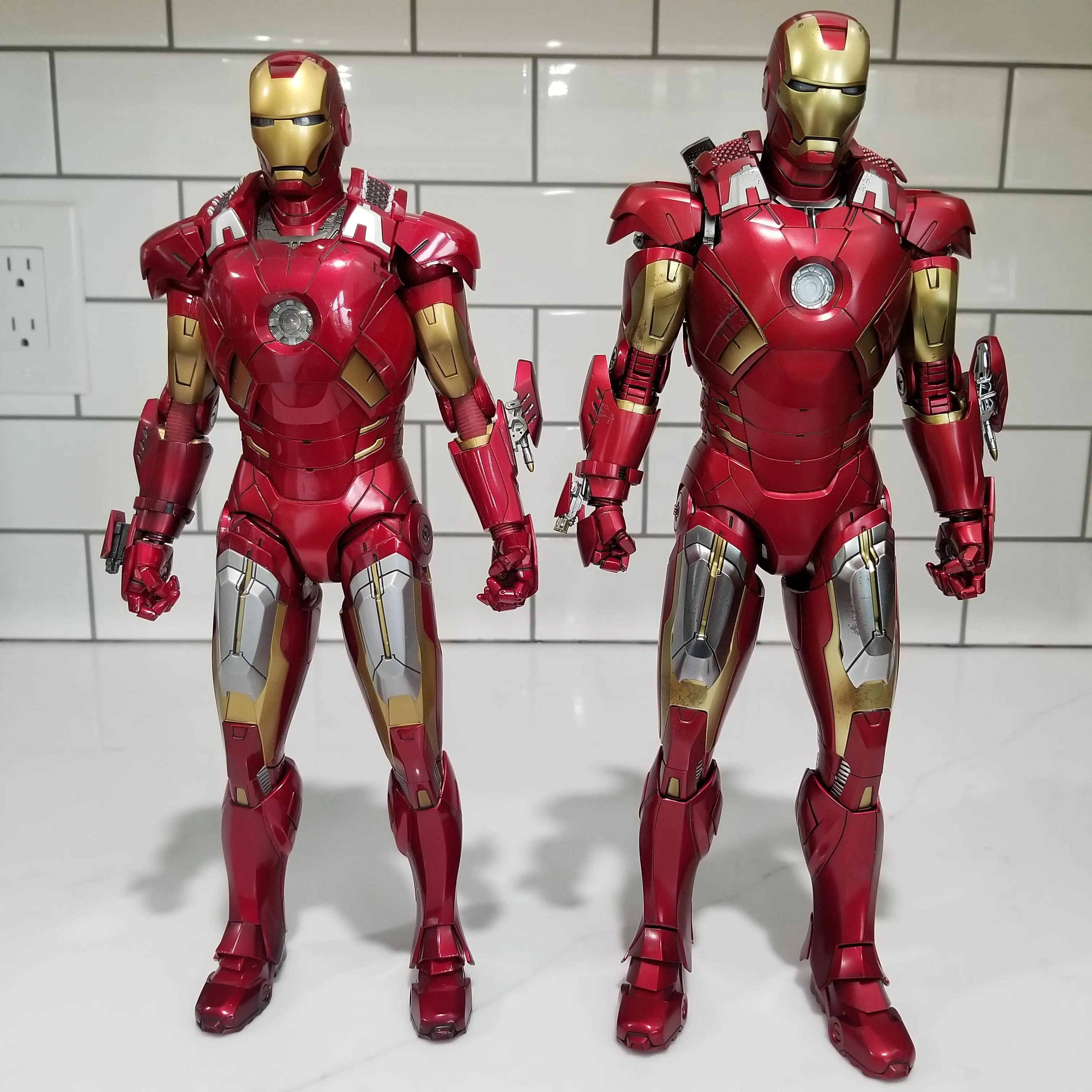

One of the primary advantages of diecast cars is their exceptional durability. The metal construction allows them to withstand wear and tear, making them ideal for play and display. Unlike plastic models that can break or crack easily, diecast cars can endure rough handling. Their robust nature also contributes to their longevity, often lasting for many years with proper care. This durability makes them a good investment, especially for collectors who want to preserve their models for future enjoyment or value appreciation. The solid build quality ensures that they can withstand the test of time.
Realistic Detailing
Diecast cars are known for their impressive level of detail. Manufacturers invest significant effort in replicating the appearance of real vehicles. This includes meticulously crafted interiors, realistic paint finishes, and accurate representations of engine components. Many models feature opening doors, hoods, and trunks, further enhancing their authenticity. This level of detail is one of the primary reasons diecast cars are highly valued by collectors and enthusiasts. The realistic detailing provides an immersive experience, making the models visually appealing and a pleasure to own.
Collectibility and Value
Diecast cars are highly collectible, and certain models can be quite valuable. Limited edition releases, rare models, and those in pristine condition often command premium prices. The collectibility aspect adds an investment dimension to the hobby. Collectors seek out models from specific manufacturers, eras, or those depicting particular vehicles. The value of a diecast car can fluctuate based on various factors, including rarity, condition, and market demand. This potential for appreciation makes diecast cars an appealing option for those looking to combine their passion for miniature vehicles with an investment opportunity.
What are Plastic Cars?

Plastic cars are primarily made from various types of plastic, such as ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) or PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride). These cars are often produced using injection molding, where plastic is heated and injected into molds. Plastic cars are generally lighter and more affordable than diecast models, making them a popular choice for children’s toys and mass-produced items. While they may not have the same level of detail as diecast cars, they offer their own set of advantages, including versatility in design and lower production costs.
Materials Used in Plastic Cars
The primary materials used in plastic cars are various polymers like ABS and PVC. These materials are chosen for their moldability, strength, and cost-effectiveness. Other materials used include paints, decals, and sometimes metal axles for the wheels. Different grades and types of plastic can be used depending on the desired level of detail, durability, and cost. Plastic cars can also incorporate transparent plastics for windows and other features. The selection of materials influences the overall quality, appearance, and functionality of the model.
Manufacturing Process for Plastic Cars
Plastic cars are typically manufactured using injection molding. This process involves melting plastic pellets and injecting them into a mold. The plastic cools and solidifies, taking the shape of the mold. The car body is then ejected, and additional components such as wheels and interiors are added. The manufacturing process is generally faster and less expensive than die-casting. Mass-produced plastic cars are created this way, making them a budget-friendly alternative to their diecast counterparts. The process allows for complex designs and a wide variety of models.
Advantages of Plastic Cars

Plastic cars offer a number of advantages. Their affordability makes them accessible to a wider audience, and their lightweight design makes them safe for children to play with. They can be produced in a wide variety of shapes, colors, and designs. The manufacturing process is generally more cost-effective than die-casting, which results in lower prices for consumers. This makes plastic cars a popular choice for toys and promotional items. They are also often more resistant to certain types of damage compared to the metal counterparts.
Affordability
One of the main advantages of plastic cars is their affordability. The manufacturing process, typically involving injection molding, is generally less expensive than die-casting. This results in lower production costs, which are passed on to the consumer. Plastic cars provide a budget-friendly option for children and collectors. Their lower price point makes them easily accessible, allowing consumers to build a collection without breaking the bank. The affordability of plastic cars makes them a great entry point to the world of miniature vehicles.
Lightweight Design
Plastic cars are significantly lighter than their diecast counterparts, making them safer for children to play with. The lightweight design also contributes to their ease of handling. Their construction makes them less likely to cause injury. This is a crucial factor for parents choosing toys for young children. Plastic cars are less likely to damage surfaces if dropped, compared to heavier diecast models. The lightweight design enhances the play experience, allowing for greater mobility and imaginative play.
Safety Considerations

The safety considerations associated with plastic cars are generally more favorable compared to diecast models. The lightweight construction reduces the risk of injury if the toy is dropped or thrown. The use of rounded edges and non-toxic materials further enhances their safety. The plastic material is less likely to chip or break, which reduces the risk of sharp edges. Careful design and production of plastic cars prioritize child safety. These are important aspects that make them a reliable and secure option for young children.
Diecast vs Plastic Cost Comparison
The cost comparison between diecast and plastic cars is a straightforward one. Diecast models generally come with a higher price tag due to their materials, manufacturing process, and level of detail. Plastic cars are considerably more affordable. The difference in cost reflects the materials used, production methods, and target market. While the price of diecast cars can vary widely depending on the model and brand, they typically represent an investment. Plastic cars offer an economical option, making them suitable for casual collectors and for children who primarily play with their toys.
Diecast vs Plastic Features Comparison
When comparing the features of diecast and plastic cars, several key differences emerge. Diecast cars often boast superior detailing, including accurate interiors, engine components, and realistic paint finishes. Plastic cars can be designed in a wider range of shapes and sizes due to the molding process. Diecast models offer a greater sense of weight and durability, while plastic cars are generally lighter and more easily customizable. The features comparison indicates which offers greater detail and quality versus flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Ultimately, your choice depends on the features which are most important to you.
Diecast vs Plastic Detailing Comparison

The detailing in diecast cars is typically superior to that of plastic cars. Diecast models are produced with an emphasis on replicating the appearance of real vehicles. Features like finely detailed interiors, accurately rendered engine components, and realistic paint finishes are common in diecast cars. Plastic cars often have a simplified aesthetic, with fewer intricate details. This difference reflects the manufacturing process and intended purpose of each type of model. Those seeking high levels of realism and accuracy will likely find diecast cars more appealing, whereas those seeking affordability and a wider range of styles may prefer plastic models.
Which Car Is Right for You
Choosing between diecast and plastic cars involves considering your specific needs and preferences. If you are a collector, or you value durability, realism, and investment potential, diecast cars are an excellent choice. If you are looking for a budget-friendly option for children, or you prioritize a lightweight design, plastic cars may be more suitable. Both types of miniature vehicles offer their own unique benefits and drawbacks. Understanding your priorities is key. Consider the desired level of detail, your budget, the age of the user, and the intended use of the car.
Factors to Consider
Several factors should influence your decision. Consider your budget, as diecast models are generally more expensive than plastic. Evaluate the intended use; are you buying for collecting or for children’s play? Assess the level of detail you desire. Think about the importance of durability and the potential for investment. Also, consider the age of the user, as some plastic cars may be safer options for younger children due to their lightweight design. Weighing these factors will help you make an informed decision that suits your specific needs and preferences.
Your Personal Preferences
Ultimately, the best type of miniature car is the one that best aligns with your personal preferences. Some collectors prefer the realism and investment potential of diecast models. Others favor the affordability and variety of plastic cars. Consider your tastes, interests, and budget when making your selection. There is no universally ‘better’ option, as both diecast and plastic cars have their place in the world of miniature vehicles. The most important thing is to enjoy your collection or provide a safe and fun toy for a child.
In conclusion, the choice between diecast and plastic cars boils down to your specific requirements and preferences. Diecast cars excel in detail, durability, and collectibility, making them a favorite among enthusiasts. Plastic cars provide affordability, versatility, and safety, which makes them ideal for children’s toys. Weigh the factors discussed in this guide to make an informed decision that enhances your enjoyment of the miniature vehicle world. Whether you choose diecast or plastic, the joy of collecting or playing with these miniature marvels remains the same. Understanding the nuances of each type will ensure you make the perfect choice for your needs.